Legal information about Investment in Vietnam

LEGAL INFORMATION ABOUT INVESTMENT IN VIETNAM
1. Policies and Guarantees on Investment
1.1. Guarantee of asset ownership
Under the Law on Investment, the Vietnamese State shall recognize and protect the ownership of assets, capital, income, other lawful rights and interests of investors. Lawful assets of investors shall not be nationalized or confiscated by administrative measures.
Moreover, the remittance of assets of foreign investors overseas is guaranteed. After all financial obligations to Vietnamese Government are fulfilled, foreign investors are permitted to transfer the following assets to abroad: (i) capital and liquidations; (ii) income from business investment; and (iii) money and other assets under the lawful ownership of the investors.
1.2. Guarantee of Business Investments
Under the Law on Investment, investors are permitted to make at their discretion decisions on business investment activities in accordance with the Law on Investment and relevant laws; to have access to and use credit funds and support funds and use land and other resources in accordance with law.
Moreover, where a new legal instrument which is promulgated provides greater investment incentives than those which the investor currently is enjoying, the investor is entitled to enjoy the investment incentives in accordance with the new legal instrument for the remaining duration in which the project is entitled to incentives.
Where a new legal instrument which is promulgated provides lower investment incentives than those which the investor has previously enjoyed, the investor shall continue to be entitled to the investment incentives in accordance with the previous regulations for the remaining duration in which the project is entitled to incentives (except changed for reason of national defense and security, social order and safety, social morals, the health of the community or environmental protection).
2. Line of Business
Prohibited business: In Vietnam, investors are entitled to conduct business investment activities in industries and trades which are not prohibited by the Law on Investment. There are some business activities in which investment is prohibited for both foreign and domestic investors, such as: business in narcotic substances, prostitution, humans or parts of human body, and some specific others.
Conditional business: In addition, there are a number of business activities in which the investment must satisfy certain conditions stipulated by the Government, such as: securities trading, insurance, casino business, logistics services, mineral trading, employment agency services, real estate trading, telecommunications services, and some specific others.
Incentives business: Conversely, the Vietnamese State shall encourage and have a policy of incentives applicable to investment in preferential investment sectors and geographical areas, such as:
-
For preferential investment sectors: high-tech activities; production of new materials, new energy, clean energy, electronics, specific agricultural machinery, automobiles, information technology, software, and some others.
-
For preferential investment geographical areas and stature: scale of capital being VND 6,000 billion; investment projects located in rural areas and employing 500 employees or more; areas with difficult socio-economic conditions; industrial zones, export processing zones, high-tech zones and economic zones, and some others.
3. Forms of Investment
The Law on Investment stipulates some forms of investment in Vietnam, namely:
-
Investment for establishment of economic organization;
-
Investment in the form of capital contribution or purchase of shares or portion of capital contribution to economic organizations;
-
Investment in the form of public private partnership contract (PPP Contract); and
-
Investment in the form of business co-operation contract (BCC Contract).
We note that, for the investment in establishment of a business organization (enterprise), the foreign investor must have an investment project and apply for a Certificate of Investment Registration under Law on Investment.
In addition, when a foreign entity does not want to invest in Vietnam, but it desires to have a business presence in Vietnam, it can set up a branch or a representative office in Vietnam.
4. Types of Enterprises
Investors may establish an economic organization (enterprise) in accordance with Law on Enterprises, including the following basic types of enterprise:
-
SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP is an enterprise owned by an individual who is responsible for its operation with all of his/her property.
-
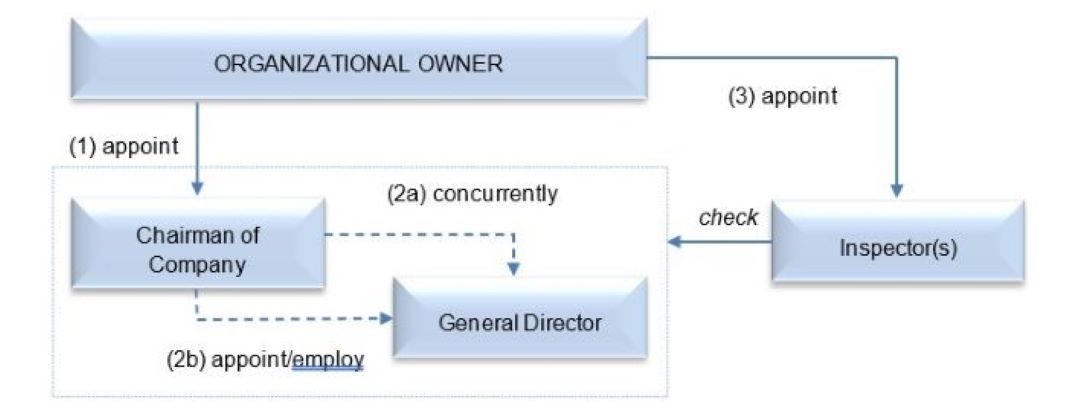
ONE MEMBER LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANY is an enterprise under the ownership of an organization or individual (the company’s owner) who is liable for the company’s debts and other liabilities up to the company’s charter capital.
-
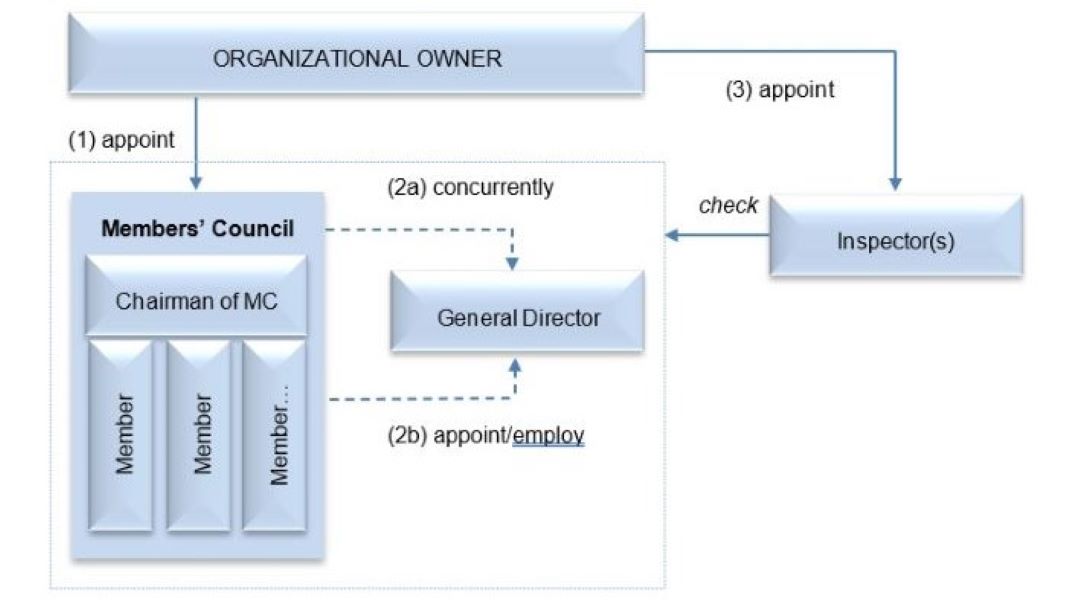
TWO AND MORE MEMBER LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANY is an enterprise under the ownership of organizations and/or individuals (the company’s members in the number of members does not exceed 50). The members are liable for debts and other liabilities of the enterprise up to the value of “contributed capital”. Stakes of members shall be transferred in accordance with the Law on Enterprises.
-
JOINT-STOCK COMPANY is a enterprise under the ownership of organizations and/or individuals (the company’s shareholders in the minimum quantity of shareholders is 03). The shareholders are only liable for the enterprise’s debts and other liabilities up to the value of “contributed capital”. Shareholders are entitled to transfer their shares to other persons in accordance with the Law on Enterprises. Joint-stock companies are entitled to issue various types of shares to raise capital.
The enterprise shall be granted the Certificate of Business registration when The application for business registration is satisfactory under Law on Enterprises. In order to operate in the conditional business, the enterprise should satisfy the legal conditions and obtain the corresponding sub-license in accordance with the law of Vietnam.
________________________________________________
@ Copyright 2015 – Công ty Luật QNT – The article is written within and under the Law on Investment No. 67/2014/QH13 dated on 26 Nov 2014 and the Law on Enterprises No 68/2014/QH13 dated on 26 Nov 2014.